A wireless sensor small enough to be implanted in the blood vessels of the human brain could help clinicians evaluate the healing of aneurysms — bulges that can cause death or serious injury if they burst. The stretchable sensor, which operates without batteries, would be wrapped around stents or diverters implanted to control blood flow in vessels affected by the aneurysms.
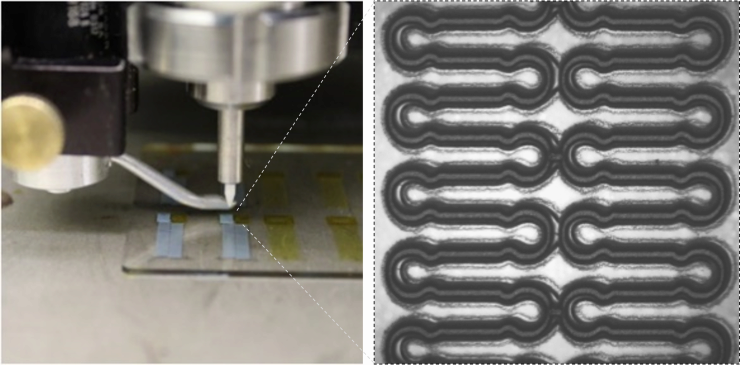
To reduce costs and accelerate manufacturing, fabrication of the stretchable sensors uses aerosol jet 3D printing to create conductive silver traces on elastomeric substrates. The 3D additive manufacturing technique allows production of very small electronic features in a single step, without using traditional multi-step lithography processes in a cleanroom. The device is believed to be the first demonstration of aerosol jet 3D printing to produce an implantable, stretchable sensing system for wireless monitoring.
“The beauty of our sensor is that it can be seamlessly integrated onto existing medical stents or flow diverters that clinicians are already using to treat aneurysms,” said Woon-Hong Yeo, an assistant professor in Georgia Tech’s George W. Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering and the Parker H. Petit Institute for Bioengineering and Bioscience. “We could use it to measure an incoming blood flow to the aneurysm sac to determine how well the aneurysm is healing, and to alert doctors if blood flow changes.”
Inserted using a catheter system, the sensor would use inductive coupling of signals to allow wireless detection of biomimetic cerebral aneurysm hemodynamics. The research was reported August 7 in the journal Advanced Science.
Monitoring the progress of cerebral aneurysms now requires repeated angiogram imaging using contrast materials that can have harmful side effects. Because of the cost and potential negative effects, use of the imaging technique must be limited. However, a sensor placed in a blood vessel could allow more frequent evaluations without the use of imaging dyes.
“For patients who have had a procedure done, we would be able to tell if the aneurysm is occluding as it should without using any imaging tools,” Yeo said. “We will be able to accurately measure blood flow to detect changes as small as 0.05 meters per second.”
The six-layer sensor is fabricated from biocompatible polyimide, two separate layers of a mesh pattern produced from silver nanoparticles, a dielectric and soft polymer-encapsulating material. The sensor would be wrapped around the stent or flow diverter, which must be less than two or three millimeters in diameter to fit into the blood vessels.
The sensor includes a coil to pick up electromagnetic energy transmitted from another coil located outside the body. Blood flowing through the implanted sensor changes its capacitance, which alters the signals passing through the sensor on their way to a third coil located outside the body. In the laboratory, Yeo and his collaborators have measured capacitance changes six centimeters away from a sensor implanted in meat to simulate brain tissue.
“The flow rate is correlated really well with the capacitance change that we can measure,” Yeo said. “We have made the sensor very thin and deformable so it can respond to small changes in blood flow.”
Use of the aerosol jet 3D printing technique was essential to producing the stretchable and flexible electronics necessary for the sensor. The technique uses a spray of aerosol particles to create patterns, allowing narrower feature sizes than conventional inkjet printing.
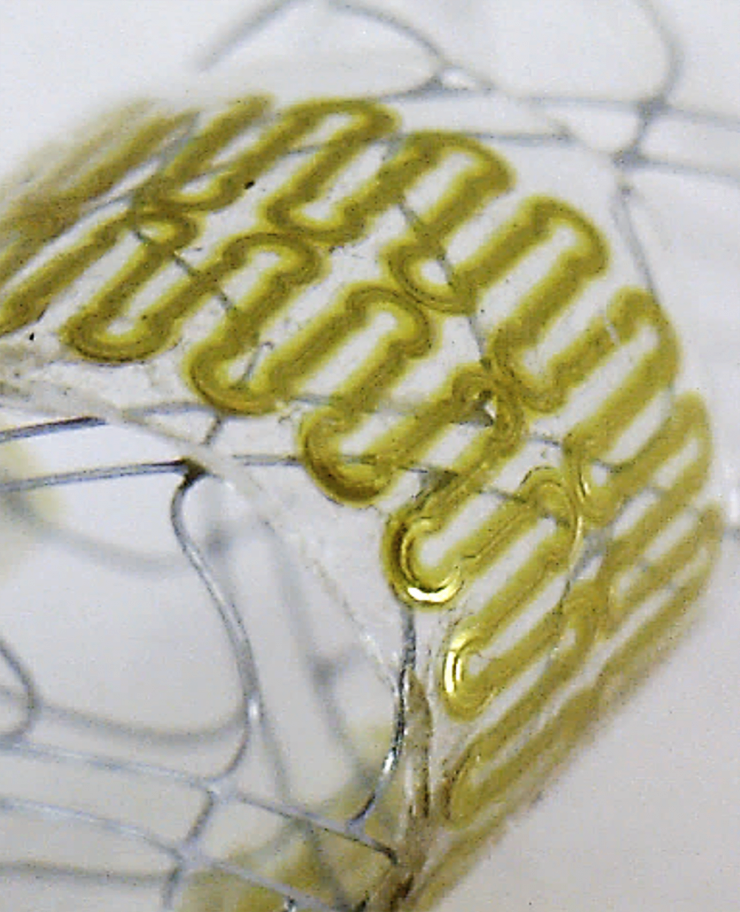
This close-up image shows details of the ultra-thin, low-profile sensor used for monitoring blood flow in the brain. (Georgia Tech Photo)
“We can control the printing speed, the printing width, and the amount of material being jetted,” Yeo said. “The parameters can be optimized for each material, and we can use materials that have a broad range of viscosities.”
Because the sensor can be fabricated in a single step without costly cleanroom facilities, it could be manufactured in higher volume at lower cost.
The next phase of the aneurysm sensor will be able to measure blood pressure in the vessel along with the flow rates. “We will be able to measure how pressure contributes to flow change,” Yeo explained. “That would allow the device to be used for other applications, such as intracranial pressure measurements.”
Yeo’s research team has also developed a flexible and wearable health monitor able to provide ECG and other information. He says the success of the monitoring technique demonstrates the potential for smart and connected wireless soft electronics based on nanomaterials, stretchable mechanics, and machine learning algorithms.
“We are excited that people are now recognizing the potential of this technology,” Yeo added. “There are a lot of opportunities to integrate this sensing mechanism into ultrathin membranes that are implantable within the body.”
Support for this research came from the Korea Institute of Industrial Technology, and a seed grant from the Georgia Tech Institute for Electronics and Nanotechnology. This work was performed in part at the Institute for Electronics and Nanotechnology, a member of the National Nanotechnology Coordinated Infrastructure, which is supported by the National Science Foundation (Grant No. ECCS 1542174).
CITATION: Robert Herbert, Saswat Mishra, Hyo, Ryoung Lim, Hyoungsuk Yoo, and Woon-Hong Yeo, “Fully Printed, Wireless, Stretchable Implantable Biosystem toward Batteryless, Real-Time Monitoring of Cerebral Aneurysm Hemodynamics” (Advanced Science, 2019) https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201901034
Research News
Georgia Institute of Technology
177 North Avenue
Atlanta, Georgia 30332-0181 USA
Media Relations Assistance: John Toon (404-894-6986) (jtoon@gatech.edu).
Writer: John Toon
